The benefits of trustless lending

Quick Take
- As the community continues its search for blockchain’s ‘killer app,’ secured lending has quickly emerged to be one of the largest and fastest growing crypto use cases
- While most crypto-secured lending to date has been done in a centralized manner, there is an evolving class of lending platforms being built on Ethereum that enable users to borrow and lend in a decentralized manner

Blockchain innovation has always been rooted in the concepts of creating, storing, and transacting in digital money. Whether it’s affordably sending money across borders or self-custodying wealth, demand for Bitcoin has largely been driven by the need for a financial service. Similarly, with Ether, demand has been a function of using the asset in investment contracts, financial derivatives, and lending agreements.
As is expected of useful money, cryptocurrencies have quickly begun to develop credit markets in which long term holders can lend out their assets to those that have a greater immediate need for them. In exchange for lending out their capital, holders are compensated for the time value of their money via an interest rate. Interest rates are essential to any valuable forms of money because they help create non zero-sum wealth as both borrowers and long term investors can reap the reward of more efficient capital allocation.
While the community continues its search for blockchain’s ‘killer app,’ secured lending has quickly emerged to be one of the largest and fastest growing crypto use cases. Genesis Capital originated over $1 billion USD in crypto-secured loans in 2018, and MakerDAO, a decentralized credit facility, originated roughly $200 million USD in Ether-collateralized loans since they launched earlier last year. [related id="1"]
Crypto-secured lending requires a borrower to post one crypto-asset as collateral in order to borrow another asset, often times fiat currency or a stablecoin. Borrowers always have to supply more collateral than the value of their loan to protect lenders from the risk of losing their money.
From a borrower’s stand point, the primary use cases for secured-lending are:
- Accessing working capital without incurring a tax liability
- Gaining leveraged long exposure to an asset they think will appreciate
- Shorting an asset they think will fall in price
- Quickly borrowing capital to take advantage of an arbitrage opportunity
On the other side, lenders earn passive interest on their long-term holdings for providing this capital.
Lending volumes to date have largely been driven by speculative trading activity and the need for short term cash. As Genesis pointed out in their Q4 2018 report, their main customers were crypto hedge funds looking to short assets like Bitcoin and Ether, proprietary trading desks that were arbitraging price discrepancies in the Bitcoin spot and futures markets, and companies that wanted short-term capital.
While most crypto-secured lending to date has been done in a centralized manner — meaning through an OTC desk or brokerage — there is an evolving class of lending platforms being built on Ethereum that enable users to borrow and lend in a decentralized manner. Through the use of smart contracts, financial services can be created in which end-users don’t need to place trust in a single operator to provide them access. By removing financial middlemen, these trustless applications stand to be much more efficient than their centralized counterparts.
Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Lending
Generally speaking, crypto-secured loans can be originated through two distinct avenues: custodial and non-custodial.
Custodial lending involves borrowing and lending assets directly from a trusted third party. This third party has complete custody of their clients’ funds at all times and acts as the counterparty within every transaction. Operators of custodial platforms also have more say in how interest rates are set as they essentially control the order book that borrowers and lenders transact through. In terms of popular asset types, most of the lending activity on custodial platforms is denominated in Bitcoin and various fiat currencies.
The most popular custodial lending avenues include centralized exchanges like Bitfinex, OTC trading desks like Genesis Capital, and credit facilities like BlockFi.
On the other hand, non-custodial lending involves borrowing and lending assets directly through smart contracts. In this case, smart contracts retain custody of the collateral throughout the entire loan life cycle, making counterparty malfeasance close to impossible. Often times, collateral is escrowed in a smart contract until either the borrower repays the loan or the loan goes into a state of default. If the borrower defaults, smart contracts can sell the underlying collateral through a DEX or a network of third parties in exchange for the principal plus interest.
In this way, aside from the technical risk associated with smart contracts not working as planned, lenders using non-custodial avenues are exposed to far less counterparty risk than they would be by going through a centralized avenue. Since a majority of non-custodial platforms leverage Ethereum’s smart contracts, most of the lending activity is denominated in Ether.
The most popular non-custodial lending avenues include MakerDAO, Dharma Lever, Compound, and dYdX. The following table compares the most popular custodial and non-custodial lending avenues across a number of key characteristics.
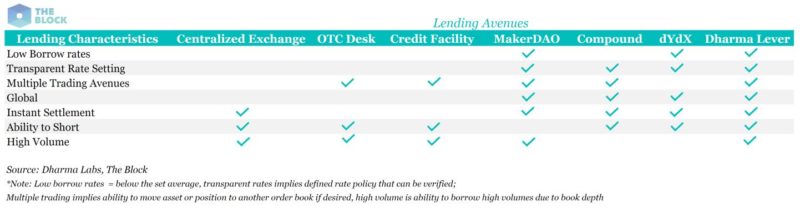
As we can see, for borrowers and lenders looking to transact in very high volumes, custodial avenues are probably best, although new solutions like Dharma Lever are coming to market to address this need.
And while there is clear demand for custodial lending within the crypto capital markets, these platforms fall victim to the same inefficiencies that plague centralized financial services. Namely, hacks related to centralized custody, lack of transparency about interest rate pricing, long settlement times, and high interest rates. And notably, these are all areas in which non-custodial solutions excel. The reason for this is clear: if a middleman is required to facilitate a transaction, they’re able to take a cut off of each step. Similarly, there’s no incentive for custodial lenders to offer transparency into their operation as the less their counterparty knows, the more value the custodial lender can extract.
While investors are increasingly locking up Ether in smart contracts to access trustless financial services, it’s going to take time for institutional capital to fully embrace open finance. For one, these platforms will need to be battle tested before institutions feel comfortable storing a large amount of capital in smart contracts. Soon, insurance products will come to market to service this need and help bridge the comfort gap. Second, the lack of KYC within non-custodial platforms is a non-starter for institutions as they’re much more strict with compliance. Solutions like Bitski are now being built to help users authenticate their identity across any decentralized application. Lastly, liquidity is still a large barrier given the fact that these financial platforms are so nascent. As non-custodial services continue to undercut centralized services across price and settlement time, these liquidity pools will start to exponentially grow.
It’s still very early days in trustless lending — a lot of liquidity needs to be formed and a great deal of infrastructure built. Notwithstanding the technical challenges faced by open financial applications more broadly, non-custodial lending solves a lot of user pain points today. Investors can take out loans against a number of different assets in sheer minutes, counterparty risk can be eliminated by smart contracts, borrowers can freely move their principal anywhere they’d like, and most importantly, all of this can be done at almost half of the cost offered by traditional lenders.
This piece was submitted through our contributor network by Max Bronstein, Marketing Manager at Dharma Labs. Dharma Labs is a Green Visor, Y Combinator, and Polychain Capital backed venture focused on building infrastructure and end-user products for an efficient, borderless, and transparent credit market. Dharma Labs built and maintains Dharma Protocol, an open-source platform that allows developers to build blockchain-based lending products that tap into this credit market. Dharma Labs recently announced Dharma Lever, a service that will allow large crypto-asset holders and institutions to trustlessly access margin from anywhere in the world, instantly, and affordably.
Max was formerly a Venture Associate at BTC Inc and graduated from UCLA with a Bachelors in Political Science and Entrepreneurship.
© 2023 The Block. All Rights Reserved. This article is provided for informational purposes only. It is not offered or intended to be used as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice.


